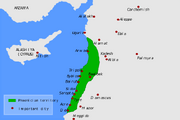
Map of Phoenicia and its major cities.
The Phoenicians were an urbanized trading people of the Mediterranean, spreading from their original homeland in the area of modern Lebanon across north Africa, Sicily, and the Iberian peninsula. Speaking a Semitic language and culturally closely related to the Canaanites to the south, the Phoenicians were city builders and traders almost from their first emergence into history. From their major cities of Tyre, Byblos, Sidon, and Arwad, the Phoenicians established, among others, the trading colonies of Carthage in North Africa, Panormus (modern Palermo) in Sicily, and Gadir (modern Cadiz) in Spain. The Phoenicians brought Egyptian and Syrian wares to the barbarian tribes of western Europe, exchanging those goods for the raw materials of those areas. Phoenician traders circumnavigated Africa on at least one occasion, and possibly traded as far as Britain. The Phoenicians, along with their mercantile interests, brought writing and accounting, and all western alphabets, including the Greek and the Latin, are descended from the Phoenician alphabet.
After the Persian empire conquered the Phoenician homeland in 539 B.C., the daughter colonies expanded under the leadership of Carthage, establishing alliances with the Berber tribes of north Africa (most notably the Numidians) and the Celtic tribes of the Iberian peninsula. The Phoenician daughter colonies came into conflict first with Greek trading colonies in the western Mediterranean, especially in Sicily, then, as the Romans began subjecting the Greek colonies, with Rome. The Romans referred to the Phoenicians as the "Punici," and to the wars between Rome and the western Phoenician alliance led by Carthage as the Punic Wars. Three great wars between Rome and Carthage occurred between 265 B.C. and 146 B.C., each ending in victory for Rome. After the Third Punic War, ending in 146 B.C., Carthage was utterly destroyed and the remaining Phoenician cities in the western Mediterranean annexed to Roman rule.